A cross-language development platform for in-memory data
- URL : https://arrow.apache.org/
- license Apache 2.0
- git : https://github.com/sncap/arrow
Powering In-Memory Analytics
Apache Arrow is a development platform for in-memory analytics. It contains a set of technologies that enable big data systems to process and move data fast.
Major components of the project include:
- The Arrow Columnar In-Memory Format
- C++ libraries
- C bindings using GLib
- Go libraries
- Java libraries
- JavaScript libraries
- Plasma Object Store: a shared-memory blob store, part of the C++ codebase
- Python libraries
- R libraries
- Ruby libraries
- Rust libraries
Apache Arrow is a cross-language development platform for in-memory data. It specifies a standardized language-independent columnar memory format for flat and hierarchical data, organized for efficient analytic operations on modern hardware. It also provides computational libraries and zero-copy streaming messaging and interprocess communication. Languages currently supported include C, C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, and Ruby.
Fast
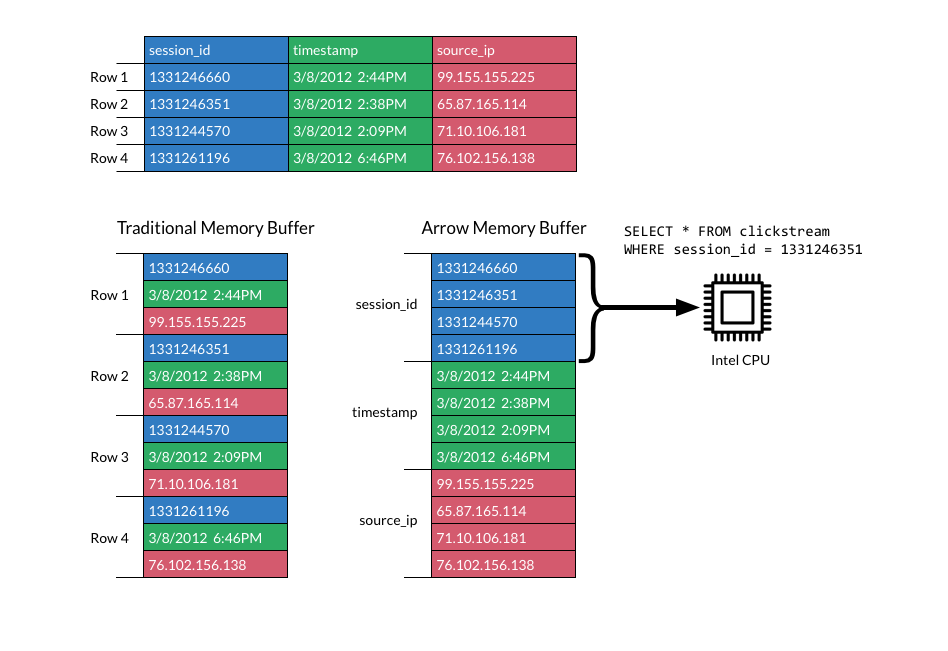
Apache Arrow™ enables execution engines to take advantage of the latest SIMD (Single input multiple data) operations included in modern processors, for native vectorized optimization of analytical data processing. Columnar layout is optimized for data locality for better performance on modern hardware like CPUs and GPUs.
The Arrow memory format supports zero-copy reads for lightning-fast data access without serialization overhead.
Flexible
Arrow acts as a new high-performance interface between various systems. It is also focused on supporting a wide variety of industry-standard programming languages. Java, C, C++, Python, Ruby, and JavaScript implementations are in progress and more languages are welcome.
Standard
Apache Arrow is backed by key developers of 13 major open source projects, including Calcite, Cassandra, Drill, Hadoop, HBase, Ibis, Impala, Kudu, Pandas, Parquet, Phoenix, Spark, and Storm making it the de-facto standard for columnar in-memory analytics.
Learn more about projects that are Powered By Apache Arrow
Performance Advantage of Columnar In-Memory
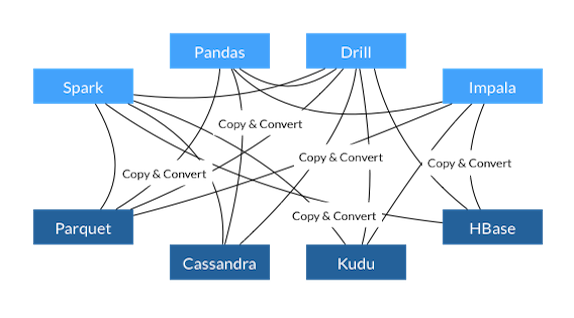
Advantages of a Common Data Layer
- Each system has its own internal memory format
- 70-80% computation wasted on serialization and deserialization
- Similar functionality implemented in multiple projects
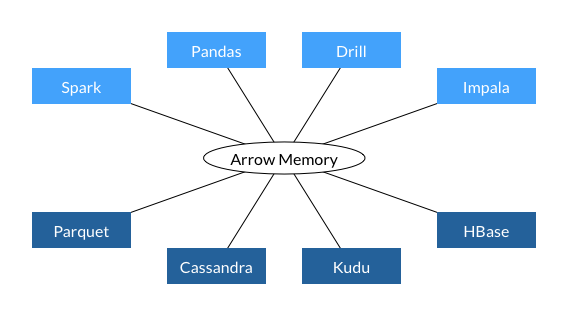
- All systems utilize the same memory format
- No overhead for cross-system communication
- Projects can share functionality (eg, Parquet-to-Arrow reader)